In this article I will display and suggest chapters, capitals and sections that are expected to be included in an ERP blueprint
Table of Contents
Any document that respects itself and even more an ERP Blueprint must have a table of content. The more detailed the table of content is, the easier it will be for the users to navigate and find information in the ERP blue print. Do not forget this is an operational document that persons will refer to constantly during the ERP project.
Introduction
This capital is not a must but I would enter it as a description of the goal and purpose of the document at hand. It must not be long but describe the reader what he or her should expect.
Terms and Definitions
This An important part of the Blueprint which will assist readers or users to get familiar with the different terms and definition used in this document. Types of terms and definitions:
- The meaning of Codes used in the document: PUR for purchase, SAL for Sales and son on
- The meaning of abbreviations
- Organizational terms
- Professional Terms
Stakeholders, Roles and Persons involved in the ERP Project
Stakeholders, persons, groups, organizations and their roles involved in the ERP project must be identified and defined in the ERP blueprint. This is a kind of a job description regarding the ERP project which defines the expectations of each in the project. The definition shall cover internal as well as external stakeholders. Another purpose is to allow an easy communication between the different roles. I would use a table that will assign each stakeholder to his or her area and expectations in the project:definitions:
| Name | Area | Contact Details | Remarks | Expectations |
Project Management in general uses the method of stakeholder register. It will definitely suitable here. Another way to describe the roles is by creating an organizational structure for project team. This will help identifying the hierarchies between the different entities.
Project Team Members
What is the difference between a project team member and a stakeholder? Very easy – a team member must perform some work or tasks and to deliver the deliverable. Whereas the CEO of the company may be a stakeholder – a person who has interest in the project. The ERP blueprint will include all functions or roles that will participate in delivering the ERP system, intern as well as extern.
| Name | Type | Area | Role |
| Mr. Harry | Intern | Management | Project Manager |
| Mrs. Smith | Intern | Purchase | Responsible for analysis and test of purchase processes |
| Mrs. Johns | Extern | Consulting | Extern consultant responsible for implementing purchase modules |
The goal of this capital is to refer anyone who has questions regarding an area in the project to a designated person.
Organizational Structure
This chapter has the goal of assisting the reader or user to get to know with the organization. This capital will contribute to the following ones. To each department or organizational unit or sub-unit included in the organizational structure include a description of its processes that are included in the ERP project.
Goals and Objectives of the ERP Project
The goals and objectives of the ERP systems are the gross expectations of the ERP system. The goals are something general which reflect the vision of the project: To automate and digitize processes in the organization or to Facilitate faster and more accurate work. The objectives and sub objectives are clearer and measurable and thus easier to define. For example:
- Enhancing stock visibility and Lowering stock costs
- Implementing stock system
- Controlling stock movements
- Counting stock levels
- Reducing manual work on purchase processes
- Introducing purchase orders to a centralized system
- Enabling a digital release process for purchase orders
- Evaluating supplier performance
- Accelerating Reaction time to customer requests
- Introducing sales orders to a centralized system
- Improving follow-ups
- And so on…
Business Process Scope of the Project
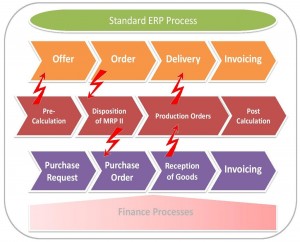 One of the most important objectives of the ERP blueprint is defining the overall ERP project scope. Why is it so important? Defining an accurate ERP project scope ensures the project includes only the work required, to complete the project successfully. How? This is done through the identification of key processes in the organization and pointing out the relevant process elements required to be covered. This will derive the most detailed work requirements of the project. For example, will HR processes be included in the ERP system? This objective will provide the a more accurate definition of the ERP project planning, control and integration.
One of the most important objectives of the ERP blueprint is defining the overall ERP project scope. Why is it so important? Defining an accurate ERP project scope ensures the project includes only the work required, to complete the project successfully. How? This is done through the identification of key processes in the organization and pointing out the relevant process elements required to be covered. This will derive the most detailed work requirements of the project. For example, will HR processes be included in the ERP system? This objective will provide the a more accurate definition of the ERP project planning, control and integration.
The scope will refer to:
- Localizations
- Departments
- Process and subprocesses
For example (this is a very very very short list):
| Business Process Description |
| Maintenance of Master data – which master data will be included in the project. |
| Maintenance of Material Master Data |
| Maintenance of Service Master Data |
| Maintenance of Vendor Master Data |
| Payment Terms |
| Stocks |
| Procurement Process |
| Request for quotation |
| Purchase orders + release of purchase orders |
| Stock entrances |
| Purchase invoices |
| Sales Processes |
| Quotations |
| Customer Order |
| Delivery notes |
| Sales Invoices |
| Production |
| MRP/Disposition and planning |
| Production proposals |
| Work Orders |
Business Process Details
Now you begin to work :). This is the heart of the ERP blue print. Here we are getting into business analysis and business requirement expected from the ERP system. After defining the business process scope, you are going deeper and define to each defined department technical data and process requirements:
- Master Data requirements
- Process transaction requirements
The next table is of course a very simple and short analysis. The more detailed you are the less questions arise during the process.
| Process: | Purchasing | Requirements | |
| Requirements for Master Data: | Vendor Data as specified in the ERP system (no special requirements) | Supplier Master Data from old ERP system shall imported into the new ERP system Identification of Numbering of purchase transactions shall be part of an organizational numbering strategy | |
| Transactions: | Request for quotation Purchase order Goods entrances Invoices | The layout of process documents (e.g. purchase order) shall be proved and approved by the stakeholders | |
| Special requirements: | Suppliers Performance Evaluation report according to the organization ISO 9001 requirements | Output of report shall be approved by the Quality department. |
This section may refer to a more detailed business documents that will provide a more detailed process analysis.
Which points you may have to cover in this section?
- Business process description including the workflow, integration with other departments and special business cases
- Master data requirements
- Resources for data for the process (users, extern systems)
- Access authorization and user policy
- Expected process output documents like purchase order operational lists
- Required reports and statistics
Opportunities for Improvements
The definition of the key processes in the organization that are included in the ERP blueprint creates the opportunity for process improvements. The ERP system offers many different functionalities that may serve the organization.
This is the right time to review them and decide which ones are relevant and will be implemented. The ERP business consultant usually analyses and assesses the intern processes and comes up with ideas and suggestions of how one can carry them out or improve them with the tools the system offers.
That requires off course analysis and assessment of the key and sub processes and changes might be needed. I personally recommend involving the key users as well as end users in this phase because they will bring the most effective inputs.
Enterprise Data
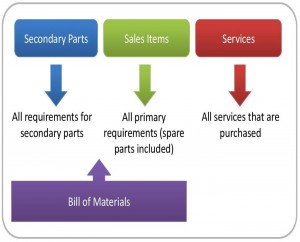 This is a critical phase that may affect the entire project. This chapter of ERP blueprint will define which enterprise data is covered in the ERP project; customer data, product data, finance movements and etc.
This is a critical phase that may affect the entire project. This chapter of ERP blueprint will define which enterprise data is covered in the ERP project; customer data, product data, finance movements and etc.
The chapter shall refer to the data conversions, integration planning, master data setup, data quality testing and any other data definitions.
The objective here is identify gaps between data requirments of the new system, required improvements for the enterprise data and testing of the data quality. For each area and scope of data the definition will include the type of data that will be included in the ERP project.
For example product data will be segmented with different business scopes: sub-assembly or semi-finished product, sales items, purchase items or services. One can define the relations and hierarchy between them. I link you to the next resource for more information.
ERP System Architecture
In this section you will describe the technical architecture of the ERP system; whether it is a ERP cloud based or a client server. This section shall include technical details that will allow the implementer to obtain a smooth installation. Which points you may have to cover in this section?
- Server maintenance
- Client access to the system
- Extern systems that must communicate with the ERP system
- Extern accessories like printers and barcode scanners


Comments are closed.